A Proximal Humerus Alpha Plate is a specialized orthopedic implant designed for the surgical fixation of fractures or reconstructions of the proximal (upper) part of the humerus, which is the long bone in the upper arm that connects the shoulder to the elbow.
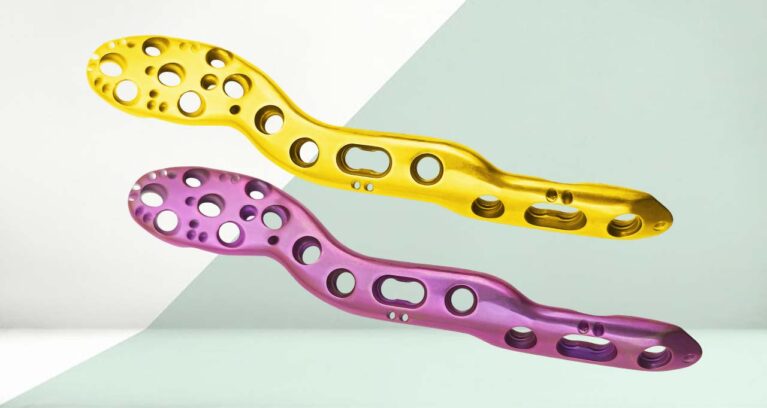
The Proximal Humerus Alpha Plate is a contoured metal plate, typically made of stainless steel or titanium, used to stabilize fractures of the upper humerus, especially those near the shoulder joint. It is anatomically shaped to conform to the natural curvature of the proximal humerus.
Key Features:
Anatomical Design:
- Pre-contoured to match the natural shape of the proximal humerus.
- Minimizes soft tissue irritation and provides a better fit.
Locking Holes:
- Includes multiple locking holes for locking screws, which provide rigid internal fixation.
- Helps maintain stability even in osteoporotic (weak) bones.
Screw Options:
- Supports both locking and non-locking screws.
- Allows angular stability and helps reduce micromovement at the fracture site.
Low-Profile Plate:
- Reduces the risk of soft tissue damage and impingement under the skin.
Multiple Screw Configurations:
- Supports multi-directional screw placement, particularly in the humeral head to ensure strong fixation.
Clinical Applications / Uses:
- Proximal humeral fractures (especially 2-part, 3-part, or 4-part fractures).
- Comminuted fractures (broken into several pieces).
- Fractures involving osteoporotic bone, common in elderly patients.
- Malunions or nonunions of previous humeral fractures.
- Humeral head reconstruction or tumor resection cases.
Advantages:
- Provides strong mechanical stability, especially in osteoporotic bones.
- Allows for early mobilization and rehabilitation.
- Reduces the risk of malalignment due to anatomical contouring.
- Enhances fracture healing by maintaining proper anatomical alignment.
- Minimizes the need for additional bone grafting in many cases.
Key Features of Proximal Humerus Alpha Plate (Detailed)
Anatomical Contouring
- The plate is pre-shaped to fit the natural curvature of the proximal humerus, especially around the humeral head and neck.
- This improves contact with the bone surface, enhances alignment, and reduces the need for manual bending during surgery.
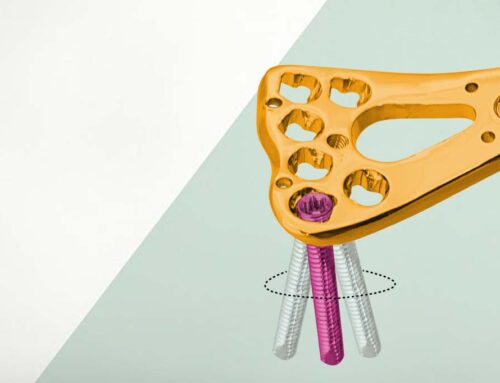
Locking Screw Technology
- Equipped with multiple locking holes for locking screws.
- Locking screws thread into the plate, creating a fixed-angle construct that provides rigid internal fixation, even in osteoporotic or comminuted bones.
- Helps maintain screw stability in cases where traditional screws might loosen.
Multi-directional Screw Insertion (Polyaxial Locking)
- Allows screws to be placed at different angles into the humeral head.
- Enables surgeons to target specific bone fragments and maximize purchase in healthy bone.
- Improves fragment capture and prevents screw cut-out into the joint.
Low-Profile Design
- Designed to be thin and streamlined, minimizing implant prominence under the skin and soft tissue.
- Reduces the risk of soft tissue irritation and postoperative complications like subacromial impingement.
Support for Bone Healing
- Includes multiple fixation points in the humeral head and shaft, distributing stress and improving load sharing.
- Aids in early mobilization, which is critical for functional recovery.
Combination of Locking and Cortical Screw Holes
- The shaft portion of the plate supports both locking and cortical screws.
- This offers flexibility: locking screws for angular stability and cortical screws for compression and pull-out resistance.
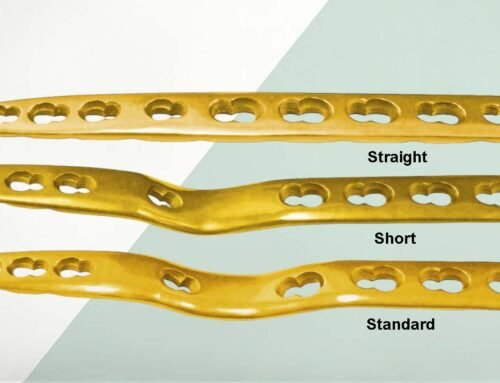
Bilateral (Left/Right) Design Variants
- Available in left and right configurations to precisely match the patient’s anatomy.
Material Composition
- Made from biocompatible materials such as titanium alloy or stainless steel.
- Offers high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with imaging (CT/MRI).
Suture Holes or Suture Slots (Optional)
- Some designs include small holes or slots for rotator cuff tendon sutures.
- These help reconstruct the soft tissue envelope, especially in rotator cuff injuries.