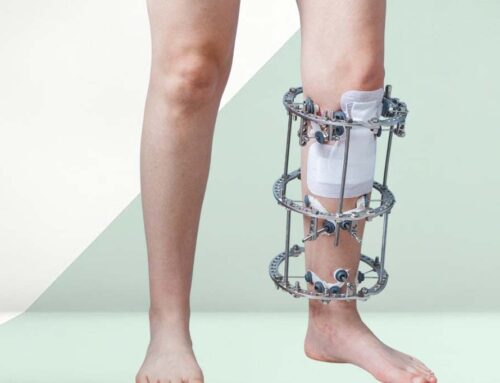
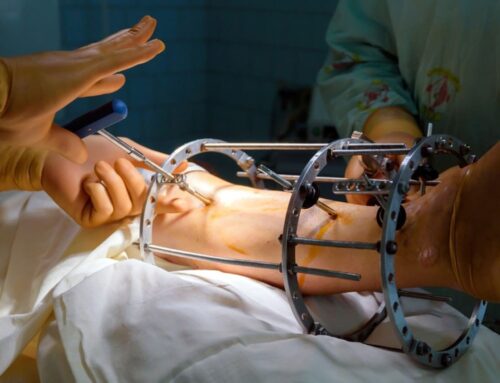
A Tutor Set (External Fixation) is a specialized orthopedic device set used to externally stabilize bone fractures, especially in trauma and emergency situations. It provides temporary or long-term fixation for fractured bones without the need for internal implantation, making it ideal for open fractures, infected fractures, or where internal fixation is risky.
Key Components of a Tutor Set
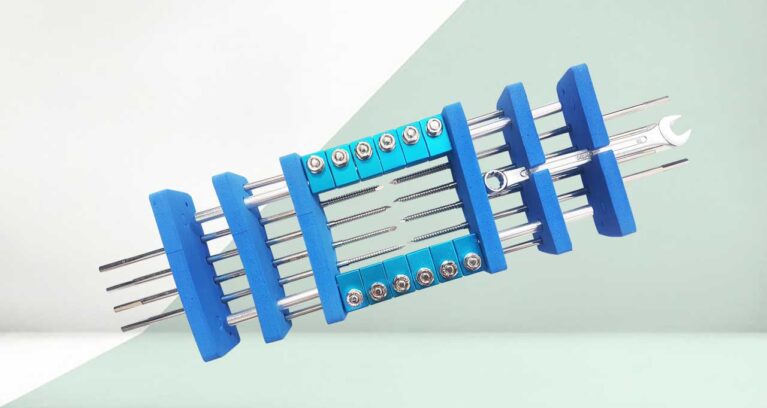
A Tutor Set for external fixation is made up of multiple mechanical components that work together to provide rigid stabilization of fractured bones from outside the body. Each component has a specific function in connecting bone segments and ensuring proper alignment during healing.
Schanz Screws (Fixation Pins)
- Description: Threaded metallic rods (partially or fully threaded) inserted into bone through the skin.
- Material: Stainless steel or titanium.
- Function: Anchor the bone segments to the external frame, Provide strong grip inside the bone cortex.
- Features: Available in various lengths and diameters (e.g., 4 mm, 5 mm, 6 mm). Often self-drilling or self-tapping. Cannulated versions available for guided insertion.
Connecting Rods (Linking Bars)
- Description: Long, cylindrical bars that connect multiple Schanz screws externally.
- Material: Carbon fiber (radiolucent for clear X-rays), Aluminum (lightweight), Stainless steel (high strength).
- Function: Provide the main framework for the fixator, Ensure alignment and stability.
- Sizes: Vary in length (e.g., 100 mm to 500 mm) and diameter (e.g., 8 mm, 11 mm).
Clamps
- Types:
- Single Pin Clamps – Connect one Schanz screw to a rod.
- Double Pin Clamps – Connect two Schanz screws to one rod.
- Universal Clamps – Allow angular and directional flexibility.
- Rod-to-Rod Clamps (Tube-to-Tube Couplings) – Join two rods together.
- Material: Stainless steel or aluminum alloy.
- Function: Securely lock Schanz screws and rods together. Allow angulation and repositioning of the fixator frame.
Tube-to-Tube Couplings (Rod Connectors)
- Description: Devices used to join two rods at various angles.
- Function: Create multi-planar fixations. Build complex frame constructs, especially in limb lengthening or deformity correction.
- Types: Straight couplers, Hinged couplers, Adjustable angle couplers.
Drill Sleeves and Guides
- Description: Precision tools used during screw placement.
- Function:
- Assist in accurate drilling and placement of Schanz screws.
- Protect soft tissues during insertion.
- Features:
- Cannulated for guided pin insertion.
- Compatible with handle and drill systems.
Wrenches and Instruments
- Types: T-handle wrench, Hex keys (Allen keys), Open spanners.
- Function: Tighten or loosen clamps, nuts, and rods. Assemble and disassemble the fixator frame.
- Material: Hardened stainless steel for strength and durability.
Rod-to-Pin Couplings
- Description: Small joints or nuts that connect a pin to a rod where a clamp is not used.
- Function: Allow angular adjustment between rod and pin. Used in simpler or emergency fixator constructs.
Optional Components
- Hydraulic Distractors: For controlled bone separation in limb lengthening.
- Ball-joint clamps: Allow multi-directional adjustment.
- Angular hinges: For deformity correction applications.
- Crossbars or side bars: Provide lateral or additional frame strength.
Common Uses of a Tutor Set (External Fixation)
The Tutor Set (External Fixation) is extensively used in orthopedic trauma care, limb reconstruction, and infection management. It plays a crucial role in stabilizing fractures from outside the body, particularly when internal fixation is not feasible or advisable.
Open Fractures with Soft Tissue Damage
- Explanation: In open (compound) fractures, the skin and soft tissue are breached, exposing bone to the environment.
- Why Tutor Set Is Used:
- Prevents contamination of the fracture site.
- Allows easy access for wound cleaning, dressing, or debridement.
- Reduces risk of infection compared to internal implants.
- Example: Tibial shaft open fracture from a road accident.
Temporary Stabilization in Polytrauma Patients
- Explanation: In patients with multiple injuries (polytrauma), initial stabilization of fractures is essential.
- Why Tutor Set Is Used:
- Quick application to control bleeding and pain.
- Temporarily immobilizes limbs while patient is stabilized for further surgery.
- Ideal for use in emergency or battlefield settings.
- Example: A patient with head trauma, chest injury, and femoral fracture.
Bone Lengthening Procedures (Distraction Osteogenesis)
- Explanation: Gradually increasing the length of a bone through controlled traction.
- Why Tutor Set Is Used:
- External fixators provide adjustable, controlled distraction.
- Tutor sets can be configured for limb lengthening with special distraction devices.
- Example: Congenital limb length discrepancy in children.
Nonunion or Delayed Union of Fractures
- Explanation: When a fracture fails to heal or heals slowly.
- Why Tutor Set Is Used:
- Provides rigid, dynamic stabilization to stimulate healing.
- Allows compression across the fracture site.
- Avoids disturbing poorly healing bone.
- Example: Atrophic nonunion of the humerus.
Infected Fractures or Osteomyelitis
- Explanation: Bone infections can complicate fractures or post-operative cases.
- Why Tutor Set Is Used:
- Avoids placing metal hardware inside infected bone.
- Allows wound access for cleaning and antibiotic delivery.
- Stabilizes bone without interfering with infection management.
- Example: Infected tibial fracture after previous implant failure.
Pediatric Fractures with Growth Plate Concerns
- Explanation: In children, preserving the growth plate is critical.
- Why Tutor Set Is Used:
- Avoids disturbing the growth plate.
- External application avoids the need for internal implants.
- Can be adjusted as the child grows.
- Example: Femoral fracture near the distal growth plate in a 9-year-old.
Complex or Comminuted Fractures
- Explanation: Fractures involving multiple bone fragments or severe dislocation.
- Why Tutor Set Is Used:
- Customizable frame provides multi-planar support.
- Maintains alignment while fragments stabilize.
- Offers better management than simple cast or splint.
- Example: Pelvic or acetabular fracture with displacement.
Limb Deformity Correction
- Explanation: Used to gradually correct angular, rotational, or length deformities.
- Why Tutor Set Is Used:
- Can be used with adjustable hinges and rods.
- Allows controlled correction without open surgery.
- Example: Post-traumatic bowing of tibia (genu varum).
Joint Fusion (Arthrodesis) Support
- Explanation: When a joint needs to be surgically fused due to arthritis or infection.
- Why Tutor Set Is Used:
- Maintains bone alignment and compression across joint surfaces.
- Avoids deep internal implants in high-risk patients.
- Example: Ankle arthrodesis in diabetic foot infection.
Benefits of a Tutor Set (External Fixation)
The Tutor Set (External Fixation) is widely recognized in orthopedic and trauma surgery for its versatility, safety, and effectiveness. It provides external bone stabilization without the need for internal implants, offering several clinical, surgical, and patient-related advantages.
Minimally Invasive Application
- Detail: Requires only small incisions for pin or screw insertion.
- Benefit: Less soft tissue damage, Minimal bleeding and shorter surgical time, Reduced postoperative pain and scarring.
- Use Case: Ideal for open or contaminated wounds where internal hardware is risky.
Infection Control and Wound Access
- Detail: Hardware is placed outside the body, away from the fracture site.
- Benefit:
- Low risk of deep infection.
- Easy access for wound dressing, debridement, or vacuum-assisted wound therapy.
- Use Case: Open fractures, infected nonunions, osteomyelitis cases.
Adjustable and Dynamic Fixation
- Detail: Components like rods and clamps can be adjusted after application.
- Benefit:
- Allows post-operative correction of alignment.
- Facilitates dynamic compression or distraction at the fracture site.
- Use Case: Limb lengthening, deformity correction, or delayed healing.
Customizable and Modular Design
- Detail: Tutor Set includes interchangeable components for diverse configurations.
- Benefit:
- Can be tailored to fit different bone sizes, fracture patterns, and anatomical regions.
- Suits both upper and lower limbs, pediatric or adult cases.
- Use Case: Segmental fractures, multiple limb injuries, or complex trauma.
Cost-Effective (Reusable Instrumentation)
- Detail: Most instruments and fixator frames are made of sterilizable metal.
- Benefit:
- Reusable in multiple cases, reducing long-term hospital costs.
- Economical for resource-limited settings.
- Use Case: Government hospitals, teaching institutions, rural healthcare units.
Radiolucency (Carbon Fiber Rods)
- Detail: Some Tutor Sets include carbon fiber connecting rods.
- Benefit:
- Enables clear X-ray, CT, or fluoroscopy imaging during and after surgery.
- Helps monitor fracture alignment and healing progress.
- Use Case: Follow-up imaging in complex fractures.
Preserves Joint and Growth Plate Integrity
- Detail: External fixation avoids placing screws across joints or growth plates.
- Benefit:
- Reduces risk of joint stiffness or deformity in children.
- Protects physiological movement and growth potential.
- Use Case: Pediatric fractures, peri-articular fractures.
Versatile for Temporary or Definitive Treatment
- Detail: Can be used either short-term or as final fixation.
- Benefit:
- Acts as a bridge to internal fixation.
- In some cases, allows complete bone healing externally without further surgery.
- Use Case: Temporary fixation in polytrauma or long-term deformity correction.
Enables Early Mobilization
- Detail: Rigid fixation outside the body stabilizes the bone without limiting adjacent joint movement.
- Benefit:
- Encourages early physiotherapy and functional recovery.
- Reduces complications related to immobility.
- Use Case: Weight-bearing tibial fractures, elderly patients with hip injuries.
Role of Tutor Set (External Fixation) in Orthopedic Implants
The Tutor Set (External Fixation) plays a critical and unique role in orthopedic implant systems. While most orthopedic implants (like plates, nails, and screws) are placed internally, a Tutor Set is used to stabilize fractures externally, making it indispensable in specific clinical situations where internal implants may not be ideal or possible.
Immediate and Temporary Fracture Stabilization
- Role: Acts as a rapid-response tool in trauma and emergency settings.
- Purpose: Temporarily stabilizes fractured bones before definitive surgery.
- Example: In polytrauma patients, the tutor set can stabilize fractures while other life-threatening injuries are managed.
Safe Alternative When Internal Fixation Is Contraindicated
- Role: Provides a secure fixation method without inserting metal into the body.
- Purpose: Avoids deep infection risk in cases like open fractures or infected wounds.
- Example: Used in osteomyelitis, infected nonunions, or wound dehiscence.
Versatile Tool in the Orthopedic Implant System
- Role: Complements other implants in staged surgeries.
- Purpose: Can be used as a standalone solution or as a bridge to internal fixation.
- Example: Applied initially in unstable fractures, then replaced by a plate or intramedullary nail after soft tissues recover.
Facilitates Bone Lengthening and Deformity Correction
- Role: Enables controlled bone growth and realignment.
- Purpose: Used in distraction osteogenesis and angular correction.
- Example: Gradual limb lengthening in congenital short limb cases or post-traumatic deformities.
Pediatric and Growth Plate Protection
- Role: Prevents damage to growth plates in children.
- Purpose: Avoids long-term growth disturbances.
- Example: Pediatric femoral fracture where plating would endanger the physis (growth plate).
Enables Post-Operative Adjustability
- Role: Provides dynamic fixation during healing.
- Purpose: Surgeons can adjust alignment or compression after surgery.
- Example: Fine-tuning fracture compression or correcting misalignment during recovery.
Supports Complex and Multi-Fragmentary Fractures
- Role: Maintains stability in fractures not easily treated with internal implants.
- Purpose: Allows customized frame construction for complex anatomy.
- Example: Severe comminuted tibial fractures or pelvic ring injuries.
Encourages Early Mobilization
- Role: Allows functional recovery without rigid internal devices.
- Purpose: Promotes movement of adjacent joints while the fracture heals.
- Example: Weight-bearing in external fixated tibial shaft fractures in early stages.